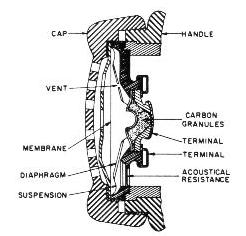
Carbon Microphone:
|
|
Operating
Principle:
- The movement of the diaphragm
compresses carbon
granules, varying the electrical current.
Advantages:
- Cheap to manufacture
- Rugged
Disadvantages:
- Requires external power source
- Limited frequency range
- Limited sensitivity
|
|
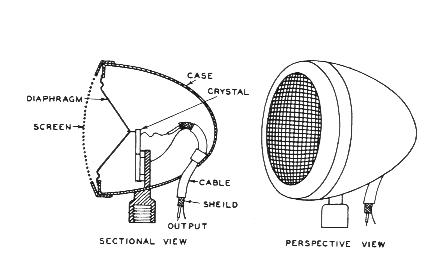
Piezo
Microphone:
|
|
Operating
Principle:
- The movement of the diaphragm bends a
crystaline
materiel, varying the electrical current generated. (Same principle as
a BBQ
starter wand.)
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
- Fragile
- High electrical impedance limits
cable length
|
|
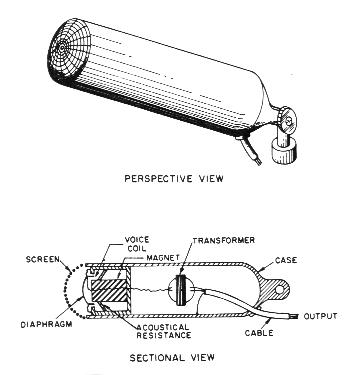
Dynamic
Microphone:
|
|
Operating
Principle:
- The movement of the diaphragm causes
a small coil of
wire to move in a magnetic field, varying the electrical current
generated.
(Same principle as bicycle dynamo.)
Advantages:
- Good quality for reasonable price
Disadvantages:
- Susceptible to external magnetic
fields (hum)
- Magnet is heavy
- Magnetic shielding is heavy
- Inertia of coil limits sensitivity
|
|
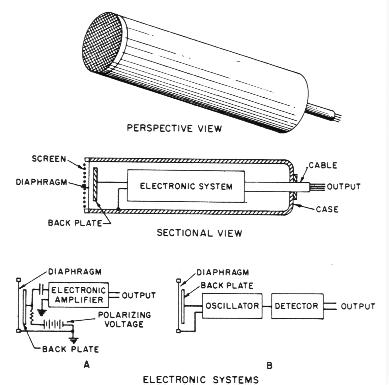
Condensor
Microphone:
|
|
Operating
Principle:
- The movement of the charged diaphragm
causes a change
in electrical capacitance, varying the electrical current generated.
Advantages:
- Thin diaphragm is light
- -- good sensitivity
- -- good high frequency response
- Can be made small
Disadvantages:
- Requires external voltage source
- Expensive to manufacture
|
|
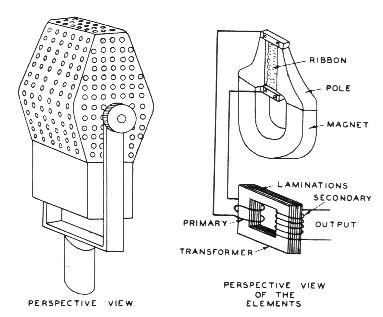
Ribbon
Microphone:
|
|
Operating
Principle:
- The movement of the ribbon within a
magnetic field,
varies the electrical current generated.
Advantages:
- Good high frequency response
Disadvantages:
- Fragile to mechanical shock, wind,
voice pops
- Very low electrical impedance
requires
transformer
|

